Philosophy is the basis of different aspects of education. If we look at the aims, curriculum, textbooks, methods of teaching, class discipline, timetable, teacher, headmaster, we find that they are all determined by philosophy. Philosophy and education are interrelated and interdependent and their salient features of relationship are as under:
Philosophy and Aims of Education
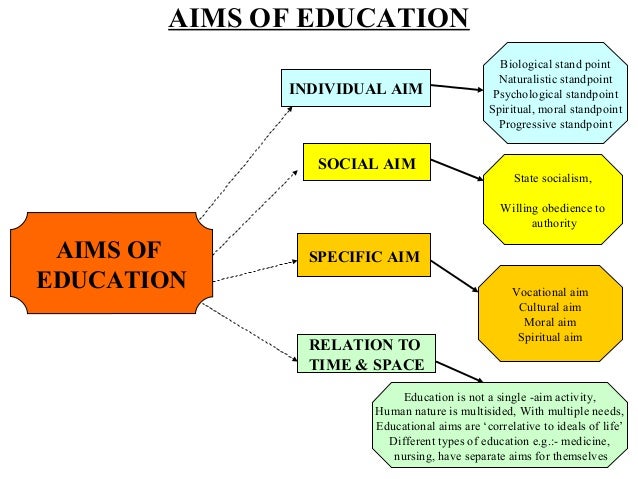
Education, being a planned activity, has a number of aims. The aims of education are related to the aims of life. These aims are formulated by the philosophy of that time. In the words of Bode, “Unless we have some guiding philosophy in the determination of objectives, we get nowhere at all”. Philosophy formulates what should be the end of life and education offers suggestions how this end is to be achieved. Different philosophies of education prescribe different aims of education. Idealism, Naturalism and Pragmatism are three distinctive philosophies and each one of them, recommends distinctive aims of education. Idealism believes in self-enhancement, naturalism prefers self-preservation,[shc_shortcode class=”shc_mybox”] pragmatism recommends socialisation of an individual. Similarly, aims of education have been different in different countries. For example, in India freedom, equality, fraternity and justice are the main aims of education. While in our neighbouring country China, the aims of education is to make the individual useful and subservient to the interest of the nation. Thus it is philosophy that makes education a purposeful activity by determining the directions and aims of education.[/shc_shortcode]
Philosophy and Curriculum

Curriculum is the total programme of giving education. Through it, desired behavioural changes are sought to be achieved to attain the goals of life and education as determined by a particular philosophy. It is philosophy which decides why a particular subject and activity should be included in the curriculum. Curriculum may be deemed as the practical side of philosophy. It is the means through which we realise the aims of education. Briggs has aptly remarked, “It is just here that education seriously needs leaders who hold a sound comprehensive philosophy, of which they can convince others and who can direct its consistent application to the formulation of appropriate curriculum.” The philosophy of a country at a particular time determines the curriculum in which such subjects, activities and experiences are included to meet the emerging demands of the society. [shc_shortcode class=”shc_mybox”]Various philosophies such as idealism, naturalism, pragmatism etc. have influenced curriculum in varying degrees. Idealists emphasis an ideal life and prescribe the study of religion, ethics, literature and humanities. Naturalists advocated physical science and direct experiences. Pragmatists lay more stress on the study of functional subjects and social sciences, they supported utilitarian, flexible and correlated curriculum. Thus philosophy is there lies in the background of every type of curriculum.[/shc_shortcode]
Philosophy and Methods of Teaching
Philosophy is also closely related to methods of teaching. In the absence of an adequate philosophy of life, the method of teaching followed by a teacher may repel the students from the subjects. Philosophy is a way of thinking and a way of working. As such, these two factors determine the nature, style and actual operation of methods of teaching. Every philosopher formulates his own methods of teaching according to his own philosophy. So every school of philosophy has its own methods of teaching. Idealism advocates question-answer method, lecture and discussion method. [shc_shortcode class=”shc_mybox”]Naturalists recommend learning by doing, heuristic method, play-way method, learning by self experiences and Montessori method. Pragmatists advocate socialised techniques, project method, problem-solving method and experimental methods.
Philosophy and Teacher

A good teacher should possess a sense of purpose in her teaching. As a teacher, one should know what his students expect, and make plans to meet those expectations. The teacher, too, has expectations about what happens in her classroom, based on the goals she is trying to accomplish. This can be achieved from the backing of a very good philosophical believe, since philosophy is concerned about the aims and ideals of education.
Philosophy helps the teacher in shaping and moulding the ideals, habits, manners, tastes and ways of life, and above all the character and personalities of the students. Every teacher is a philosopher. He influences the personality of the child and gives him a new outlook of life. A philosophical background gives teachers the power to choose the curriculum, organize the school day, and construct classroom activities.
Each philosophy determines the place of the teacher differently in the education system. For example, an idealist teacher is a man of higher ideals. He is indispensable. Naturalism accepts a teacher as a stage setter and working behind the scene. He is not to interfere in the education of the child in a direct way. According to Pragmatism, a teacher is a friend, philosopher and guide facilitating the process of growth of the child.
Philosophy and Discipline

Philosophy also determines the nature and form of discipline. [shc_shortcode class=”shc_mybox”]Whether school discipline should be strict and rigid or flexible and free is also a philosophical problem. It may be pointed out that social, political, economic and philosophical thinking of a particular country determines the nature of discipline. For example, an authoritarian government enforces rigid discipline while a democratic country gives more or less freedom of action to children in schools.[/shc_shortcode]
Philosophy and Educational Values
Philosophy has given rational and logical shapes to educational values. Values are principles or standards of behaviour; one’s judgement of what is important in life. Any change in educational values of a society will affect every aspect of the society; therefore these changes should be done by critically analysing the needs and ways of living of the people of the society. Philosophy plays a main role in analysing and preparing correct values which suits the human nature of the particular region or time.
Thus, philosophy and education are interrelated and interdependent and their salient features of relationship are as under:
-
- Philosophy is the foundation to decide the goals of life. Education then equips people suitably to achieve the said goal.
- The different educational movements which have been prevalent in history of education were led by the great philosophers.
- Philosophy determines what is worth living. Education then educates the man and prepares him for that type of life which is worth living.
- Philosophy is the theoretical side, while education is the practical side. The former is contemplative whereas the latter is dynamic.
- Philosophy suggests the values to be pursued in life. Education then inculcates those values in the learners.
- Philosophy helps in clarifying the numerous educational issues and problems.
- Philosophy provides zeal and inspiration to the teachers for accomplishing the educational tasks.
